Nearly 1 in 4 people in the U.S. have low levels of vitamin D. Though not all show symptoms, those who do face several problems. Vitamin D keeps bones strong, helps the immune system, and boosts overall health. People lacking vitamin D may feel tired, have sore bones and weak muscles. They might also feel down or depressed. It’s important to know these signs early for the right treatment, especially as this issue becomes more common.
Key Takeaways
- Almost 25% of U.S. adults are low in vitamin D.
- Many experience symptoms like fatigue, bone pain, and hair loss.
- Darker skin tones are more likely to have deficiencies due to lower vitamin D production from sunlight.
- The recommended dietary allowance varies by age, with adults needing 600 to 800 IU daily.
- Timely identification of symptoms can lead to effective treatments and improved health outcomes.
Understanding Vitamin D Deficiency
About 1 billion people worldwide don’t get enough vitamin D. This vitamin is key for bone health, helps absorb calcium, and is important for muscles to work right.
Most of our vitamin D comes from the sun. It gives us 80-90% of what our body needs through our skin. To have enough vitamin D, your blood levels should be at least 50 nmol/l. Yet, many people don’t reach this due to not enough sun or certain diets.
If you don’t get enough vitamin D, you might feel weak or have bone pain. This can lead to worse problems like osteoporosis or rickets. Older folks often need more vitamin D. It can help prevent falls by 20-30% in them.
Lacking vitamin D also links to heart, lung, bone, and metabolic problems. Muscle pain, arthritis, and chronic pain can mean you need more of it. So, vitamin D is really important for your health.
| Vitamin D Levels (ng/mL) | Status |
|---|---|
| Below 20 | Deficient |
| 21 – 29 | Insufficient |
| 30 and above | Adequate |
What Causes Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency happens for various reasons that stop us from getting enough of it. In the U.S., lack of sun plays a big part. Those in northern places or covered in clothes might not get enough sun to make vitamin D.
Not eating the right foods is another big reason. People who don’t eat animal products have a tough time getting enough vitamin D. This is because it’s mostly in foods from animals.
Some can’t absorb vitamin D well because of health issues. Conditions like Crohn’s disease or liver problems can make absorption hard. This can lead to not having enough vitamin D. Knowing these causes of vitamin D deficiency helps us deal with and prevent it.

| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Inadequate Sun Exposure | Lack of sunlight, especially in northern latitudes or among individuals who cover their skin. |
| Poor Dietary Intake | Difficulty in obtaining vitamin D from food, notably in vegans or those with restrictive diets. |
| Absorption Issues | Medical conditions that hinder the body’s ability to absorb vitamin D effectively. |
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency can cause various symptoms that affect everyday life. It’s important to know these signs for early care.
Fatigue and Tiredness
Many people feel very tired when they lack vitamin D. These low energy levels often come from hormonal imbalances.
Bone and Back Pain
Another sign is bone pain. Without enough vitamin D, your body can’t absorb calcium well. This leads to discomfort in bones and back, making it hard to move easily.
Muscle Weakness and Aches
Weak muscles are also common with this deficiency. It can make daily tasks hard. You might have trouble climbing stairs or walking.
Anxiety and Depression
Studies show a link between low vitamin D and mood disorders like anxiety and depression. People might feel more irritable and have mood swings.
Impaired Wound Healing
Vitamin D is key for fixing cells. If you’re low, wounds might heal slower. This makes recovery from injuries or operations longer.
Hair Loss
Hair loss can happen when you don’t have enough vitamin D. This is often seen in autoimmune diseases. It’s a sign that needs attention.
Frequent Illness
Getting sick a lot might mean your vitamin D is low. Since it’s crucial for the immune system, not having enough can lead to more infections and sickness.
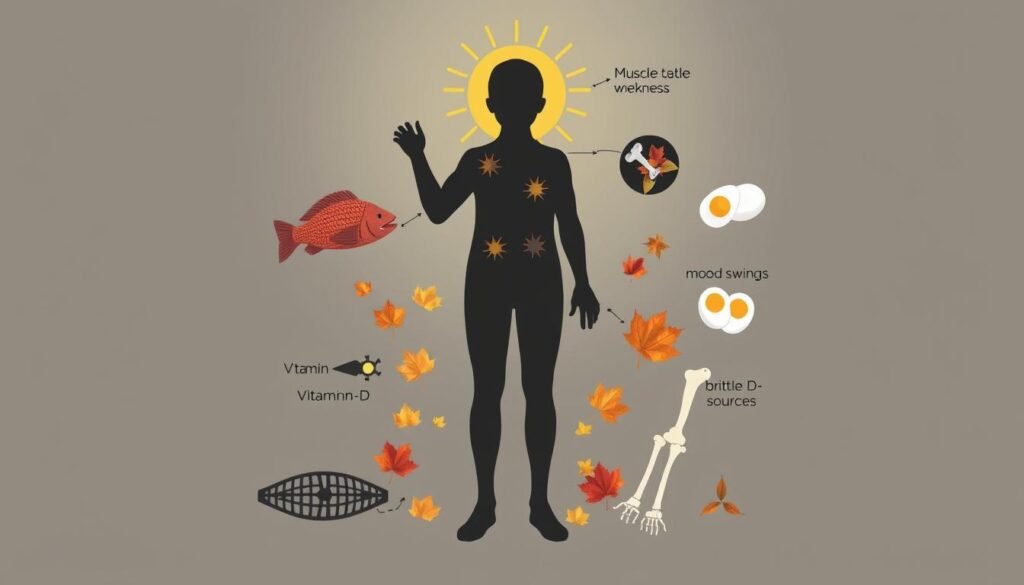
| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Persistent tiredness due to hormonal imbalances |
| Bone Pain | Discomfort from reduced calcium absorption |
| Muscle Weakness | Difficulties in physical activities |
| Anxiety | Increased irritability and mood issues |
| Impaired Wound Healing | Slower recovery from injuries |
| Hair Loss | Related to autoimmune issues |
| Frequent Illness | Higher susceptibility to infections |
The Impact of Bone Loss Due to Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D is key for our bodies to absorb calcium, keeping our bones strong. Without enough vitamin D, our bones can weaken, leading to a higher risk of osteoporosis. This deficiency speeds up bone turnover, increasing the chance of fractures related to osteoporosis.
About 5.5% of people in 27 European countries have osteoporosis. Women are more affected with a rate of 22.1%, while men have a 6.6% rate. If you lack vitamin D, you could develop osteomalacia as an adult or rickets as a child. This means your bones might become soft and deformed.
Studies show taking at least 800 IU of vitamin D daily can lower the risk of fractures. Combining this with calcium makes your bones even stronger. A specific study found that 482 to 770 IU of vitamin D daily decreases the risk of hip and other fractures by about 20%.
Not getting enough vitamin D over time can lead to serious health problems. It’s crucial to know your vitamin D levels. Eating foods high in calcium and taking supplements can help keep your bones healthy.
Identifying Risk Factors for Vitamin D Deficiency
It’s important to know why some people lack enough vitamin D. This vitamin is key for staying healthy. Many factors influence the chances of not getting enough. These include skin color, age, and what you eat.
Skin Tone and Sun Exposure
People with darker skin have a harder time making vitamin D from sunlight. They have more melanin, which blocks production. So, they need to spend more time in the sun to get enough vitamin D. If they don’t, they’re more likely to not have enough of this vitamin.
Age and Dietary Factors
Getting older can also make it harder to get enough vitamin D. Older people’s skin doesn’t make vitamin D as well when it’s sunny. This can be a big problem, especially when they don’t eat certain foods. Not eating enough foods like fatty fish or fortified products can lead to not enough vitamin D. Knowing this, people can make better food choices for their health.

How to Diagnose Vitamin D Deficiency
Figuring out if someone lacks vitamin D starts by looking closely at their symptoms and risk factors. About 1 in 4 adults in the U.S. don’t have enough vitamin D. This highlights why we need good tests. A key test is the 25-hydroxy vitamin D test. It checks how much vitamin D is in the blood.
Doctors suggest this test if you’re feeling bones pain or muscle weakness. It’s also for those over 65, people who are obese, or those who don’t get much sun. Knowing if you have less vitamin D than you need is crucial for getting the right treatment.
The 25-hydroxy vitamin D test shows if your vitamin D level is too low, just right, or not enough. Labs might have different normal ranges. If you understand your results, you can better manage your health. This is especially true for folks with ongoing health issues or trouble absorbing nutrients. They are more likely to have a vitamin D deficiency.
It’s smart to keep an eye on your vitamin D level. This is key for anyone being treated for low vitamin D or at risk of it. You can test your blood at the doctor’s or with a home kit. Usually, you’ll know the results within a few days. This helps your doctor decide what to do next.
| Vitamin D Status | 25-hydroxy Vitamin D Level (ng/mL) |
|---|---|
| Deficient | Less than 20 |
| Insufficient | 20-29 |
| Adequate | 30 or more |
By testing often and knowing what your results mean, you can actively keep your vitamin D level where it should be. This is crucial for healthy bones and feeling good overall.
Treatment Options for Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is a common issue, especially in older adults. The main approach to treatment for vitamin D deficiency is through taking supplements, mainly D3. The dose varies based on how much the person lacks. Adults usually need about 800 international units (20 micrograms) daily. Meanwhile, kids need around 400 international units (10 micrograms).
Making changes to your diet is also essential. Eating vitamin D-rich foods like fortified cow’s milk, fatty fish, and egg yolks helps a lot. Knowing what to eat allows people to choose their food wisely. Not eating enough of these foods, not absorbing them well, and certain medical issues can lead to vitamin D deficiency.
Doctors may suggest specific doses of D2 or D3 after checking your 25(OH)D level. For example, children might get 1000 to 2000 international units (25 to 50 micrograms) a day. It’s important to watch how much you take. Too much vitamin A, especially from cod liver oil, can be harmful. It can cause liver problems and weak bones.
To tell if the treatment is working, keeping track of vitamin D levels is critical. Sunscreen use, while good for skin protection, can lower vitamin D creation by the sun. This makes maintaining the right levels tricky. People with ongoing health issues like chronic kidney disease need regular checks. They must adjust their supplements to stay healthy.
| Age Group | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|
| Adults | 800 IU (20 mcg) |
| Infants and Children | 400 IU (10 mcg) |
| Children with Deficiency | 1000-2000 IU (25-50 mcg) |
For deeper insights into treatment for vitamin D deficiency, check out Cleveland Clinic. They offer detailed info on this widespread health challenge.
Conclusion
It’s crucial to know if you’re low on vitamin D for your health. In the U.S., about 35% of adults don’t get enough. Vitamin D is vital for strong bones, fighting off germs, and might even help your mood. Some research links not having enough vitamin D with feeling depressed.
Getting a blood test can show if you need more vitamin D. This helps you choose the right foods and how much sun you need. The National Osteoporosis Foundation says getting enough vitamin D is very important, especially for women after menopause who are at risk for weak bones. Eating foods like cod liver oil, salmon, and fortified items can boost your vitamin D. Also, knowing your risk factors helps a lot. For more info on this, check out this link.
Taking extra steps, like supplements if necessary, can improve your health. A community that knows about vitamin D and its importance will be healthier and more vibrant.



